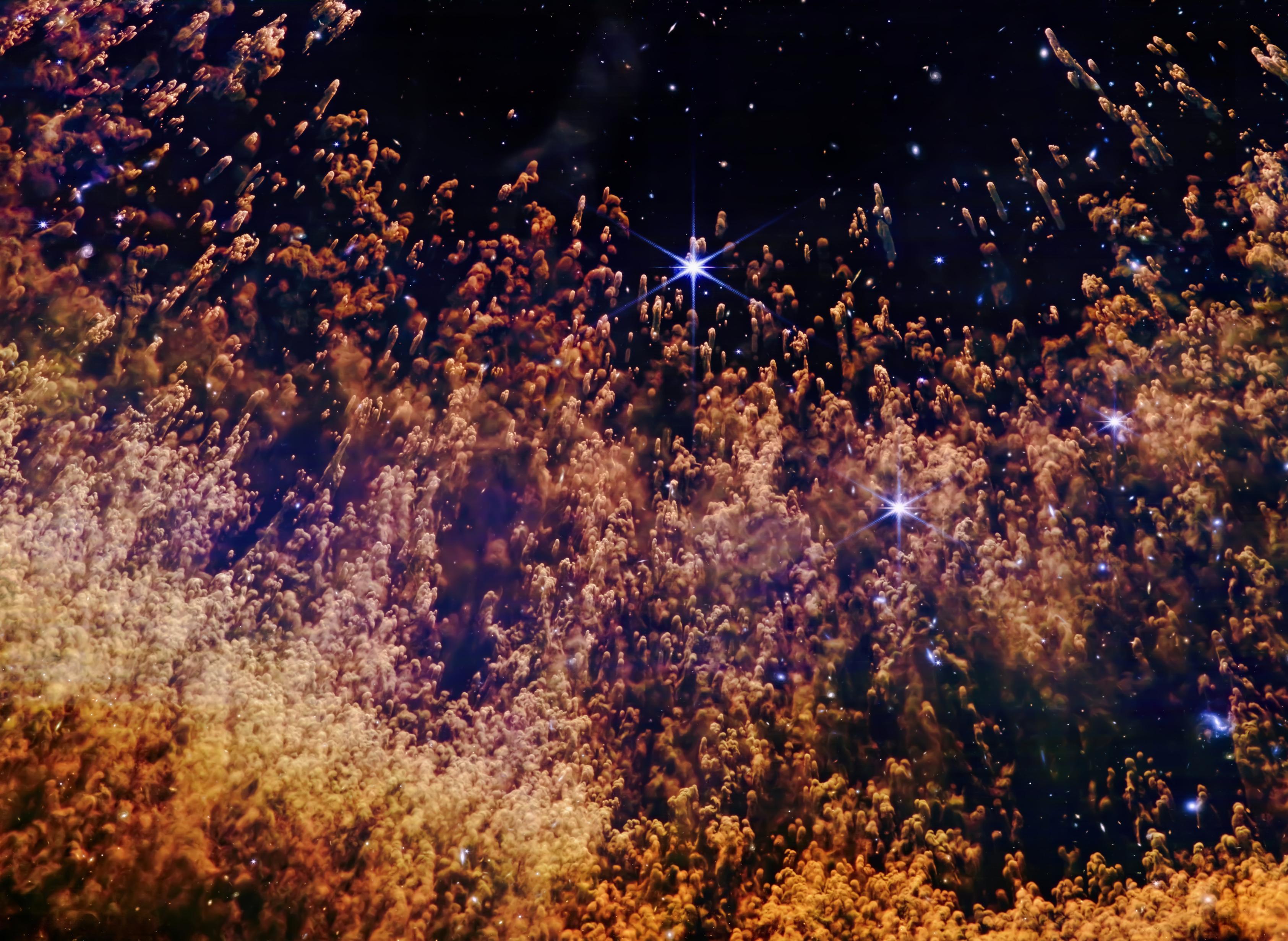
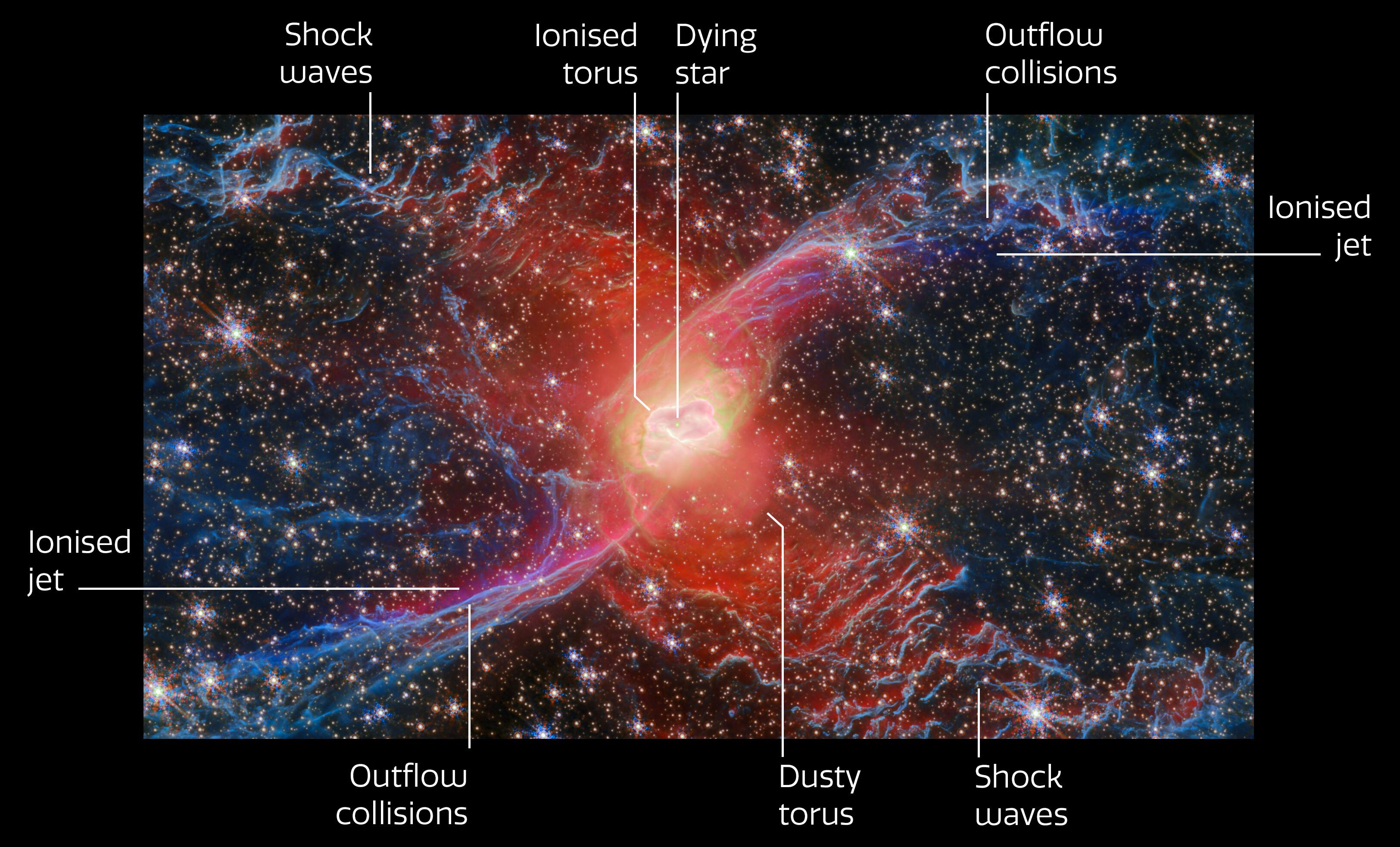
1/2 Helix Nebula (NGC 7293) - NASA/ESA JWST Space Telescope
Full size 12K: https://flic.kr/p/2rTo3xx
Credit: NASA/ESA/CSA/STScI/j.Roger/AndreaLuck CC BY
NIRCam
Imaging dust knots in a planetary nebula
2024-10-24
Filters: F115W, F187N, F212N, F356W, F444W, F470N
Colours Assigned: Blue, Cyan, Green, Yellow, Orange, Red
PI: Macarena Garcia Marin
PI Institution: Space Telescope Science Institute - ESA - JWST
Proposal ID: 6557