#BREAKING #ESETresearch identified the wiper #DynoWiper used in an attempted disruptive cyberattack against the Polish energy sector on Dec 29, 2025. At this point, no successful disruption is known, but the malware’s design clearly indicates destructive intent.
#ESETresearch attributes the attack to the Russia‑aligned #Sandworm APT group with medium confidence, based on strong overlaps in behavior and TTPs with multiple earlier Sandworm-linked wiper operations investigated by our team.
The attack struck during peak winter and the 10‑year anniversary of Sandworm’s 2015 attack on Ukraine’s power grid - the first malware-driven blackout, leaving ~230,000 people without electricity.
#ESET detects DynoWiper as Win32/KillFiles.NMO. Customers of our private ESET Threat Intelligence APT reports have already received additional technical details and IOCs to support rapid detection and response. IoC: 4EC3C90846AF6B79EE1A5188EEFA3FD21F6D4CF6
We continue to investigate the incident and broader implications. As new evidence or links to additional Sandworm activity emerge, we will share further updates to help defenders protect critical sectors.
ESET will retire its Password Manager on Oct 18, 2027, with all stored data deleted after shutdown. 🔐
Users must export credentials and migrate early as renewals and activations face strict cutoffs. ⏳
🔗 https://proton.me/blog/eset-password-manager
#TechNews #Security #Privacy #Data #Cybersecurity #Encryption #OpenSource #Passwords #Migration #UserRights #Accountability #Tech #DigitalSafety #ESET #Password #PasswordManager
ESET will retire its Password Manager on Oct 18, 2027, with all stored data deleted after shutdown. 🔐
Users must export credentials and migrate early as renewals and activations face strict cutoffs. ⏳
🔗 https://proton.me/blog/eset-password-manager
#TechNews #Security #Privacy #Data #Cybersecurity #Encryption #OpenSource #Passwords #Migration #UserRights #Accountability #Tech #DigitalSafety #ESET #Password #PasswordManager
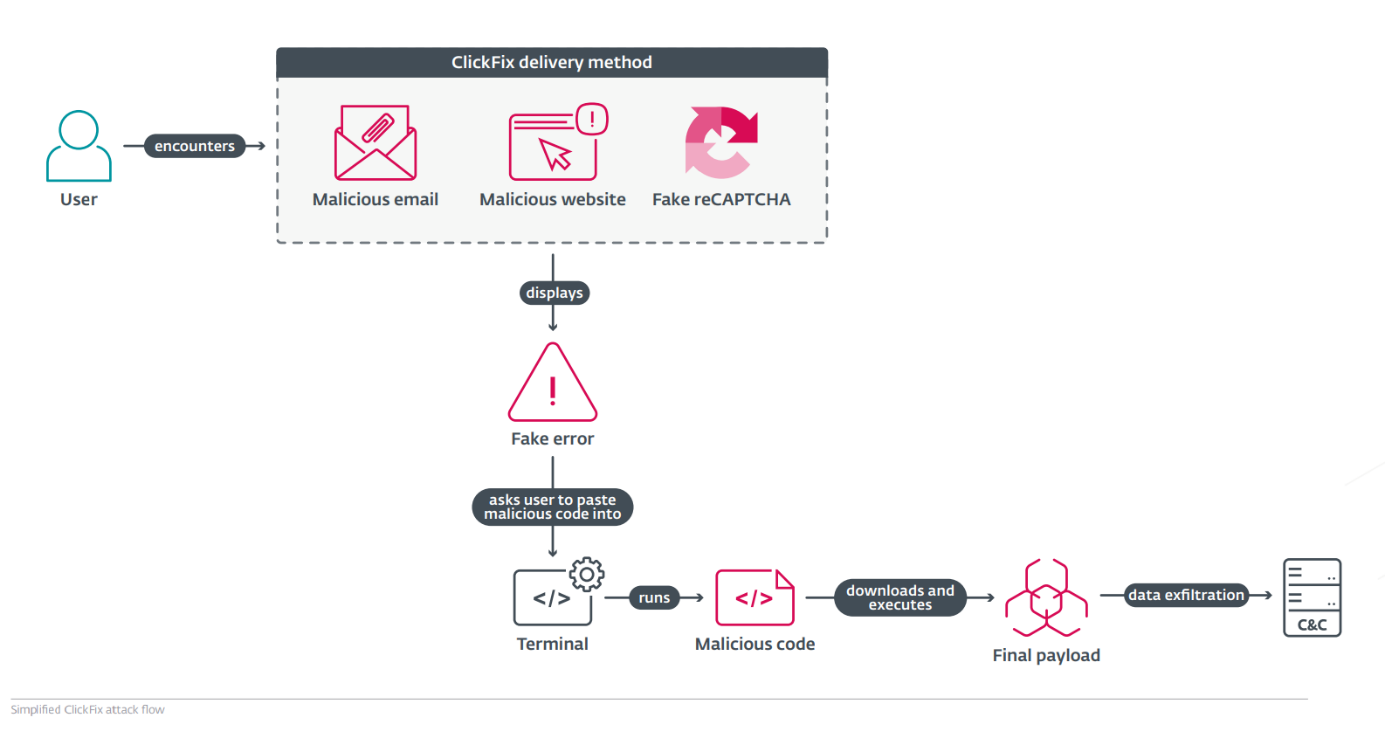
ClickFix lures users by displaying bogus error messages followed by quick fix instructions, including copy-pasting malicious code. Running the code in the victim’s command line interpreter delivers malware such as #RATs, infostealers, and cryptominers.
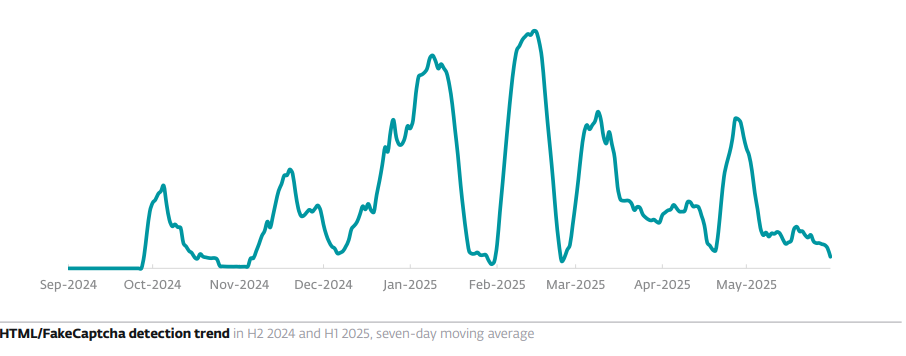
Between H2 2024 and H1 2025, ESET’s detection for ClickFix, HTML/FakeCaptcha, skyrocketed by 517%. Most detections in ESET telemetry were reported from Japan (23%), Peru (6%), and Poland, Spain, and Slovakia (>5% each).
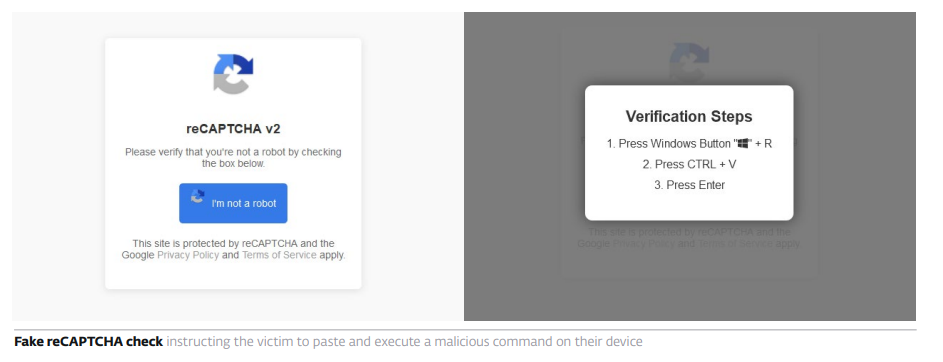
What makes #ClickFix so effective? The fake error message looks convincing; instructions are simple, yet the copied command is too technical for most users to understand. Pasting it into cmd leads to compromise with final payloads, including #DarkGate or #LummaStealer.
While #ClickFix was introduced by cybercriminals, it’s since been adopted by APT groups: Kimsuky, Lazarus; Callisto, Sednit; MuddyWater; APT36. NK-aligned actors used it to target developers, steal crypto and passwords from Metamask and #macOS Keychain.
#ClickFix uses psychological manipulation by presenting fake issues and offering quick solutions, which makes it dangerously efficient. It appears in many forms – error popups, email attachments, fake reCAPTCHAs – highlighting the need for greater vigilance online.
Read more in the #ESETThreatReport:
🔗 https://welivesecurity.com/en/eset-research/eset-threat-report-h1-2025
ClickFix lures users by displaying bogus error messages followed by quick fix instructions, including copy-pasting malicious code. Running the code in the victim’s command line interpreter delivers malware such as #RATs, infostealers, and cryptominers.
Between H2 2024 and H1 2025, ESET’s detection for ClickFix, HTML/FakeCaptcha, skyrocketed by 517%. Most detections in ESET telemetry were reported from Japan (23%), Peru (6%), and Poland, Spain, and Slovakia (>5% each).
What makes #ClickFix so effective? The fake error message looks convincing; instructions are simple, yet the copied command is too technical for most users to understand. Pasting it into cmd leads to compromise with final payloads, including #DarkGate or #LummaStealer.
While #ClickFix was introduced by cybercriminals, it’s since been adopted by APT groups: Kimsuky, Lazarus; Callisto, Sednit; MuddyWater; APT36. NK-aligned actors used it to target developers, steal crypto and passwords from Metamask and #macOS Keychain.
#ClickFix uses psychological manipulation by presenting fake issues and offering quick solutions, which makes it dangerously efficient. It appears in many forms – error popups, email attachments, fake reCAPTCHAs – highlighting the need for greater vigilance online.
Read more in the #ESETThreatReport:
🔗 https://welivesecurity.com/en/eset-research/eset-threat-report-h1-2025
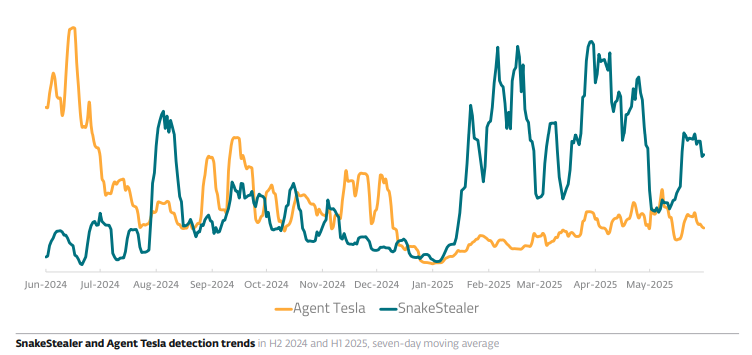
After years of dominance in #ESET’s top #infostealer statistics, the era of #AgentTesla has come to an end. It finished H1 2025 in fourth place, its numbers having decreased by 57%. The reason? It is no longer under active development.
The threat actors behind Agent Tesla have reportedly lost access to the servers with the malware’s source code. A successor appeared almost immediately – another #MaaS threat, known as #SnakeStealer or #SnakeKeylogger, has claimed the number one spot.
Recommended as a suitable replacement directly in Agent Tesla’s Telegram channel, SnakeStealer now takes up almost a fifth of all infostealer detections registered by ESET telemetry. Between H2 2024 and H1 2025, its detections more than doubled.
If you want to find out more information about this changing of the guard in the infostealer threat landscape, head on over to #ESETThreatReport: https://welivesecurity.com/en/eset-research/eset-threat-report-h1-2025