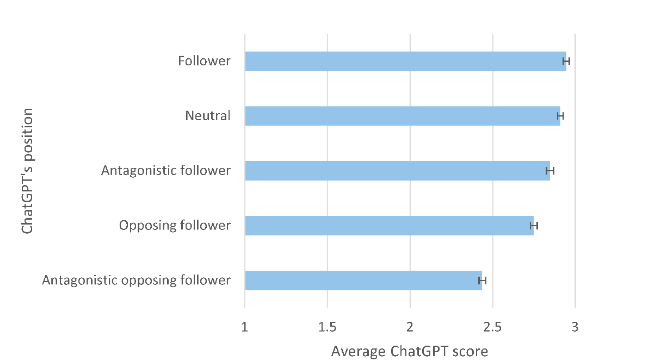
If an AI is told to "follow" a certain academic paradigm, will it rate papers differently? 🤔 A new study by Mike Thelwall et al. shows: yes. Across 8 paradigm pairs and 1,490 papers, #ChatGPT scored higher when aligned and lower when opposed, quietly penalizing ideas outside its frame:
📄 https://arxiv.org/abs/2510.22426
To me, it’s a warning - #AI trained on dominant views can undermine pluralism and create a technical illusion of one truth.