I'm just following the psycho-drama of that Board of Peace. The AP says this was the state of play at 5pm today.
(Stories are circulating that UK and Germany have also made decisions too ... )
#diplomacy #MiddlePowers
https://apnews.com/article/trump-netanyahu-gaza-board-of-peace-a4a296f736474e8c6a4edacd7109b8e5
I'm just following the psycho-drama of that Board of Peace. The AP says this was the state of play at 5pm today.
(Stories are circulating that UK and Germany have also made decisions too ... )
#diplomacy #MiddlePowers
https://apnews.com/article/trump-netanyahu-gaza-board-of-peace-a4a296f736474e8c6a4edacd7109b8e5
Canada's deal with China signals it is serious about shift from US
https://www.bbc.com/news/articles/cm24k6kk1rko
#HackerNews #Canada #China #Relations #Shift #US #Policy #International #News #Diplomacy
🆘 U.S. officials have discarded the idea of legal constraints altogether.
The day after the United States kidnapped Maduro and his wife in Venezuela,
the senior Trump aide #Stephen #Miller explained the administration’s thinking in an interview with the CNN host Jake Tapper.
“We live in a world, in the real world, Jake, that is governed by strength,
that is governed by force,
that is governed by power,”
Miller said.
“These are the iron laws of the world since the beginning of time.”
Neither Miller nor anyone else in the administration offered any real legal justification for launching a military assault on Venezuela
—an operation that killed at least 75 people.
There has been no legal justification, either,
for the plan Trump announced on social media to seize “between 30 and 50 MILLION Barrels” of Venezuelan oil.
Instead, the State Department shared an image of the U.S. president emblazoned with the words
“This is OUR Hemisphere,”
and Trump styled himself in a Truth Social post as the
“Acting President of Venezuela.”
Now, the administration has begun to turn its sights on #Greenland.
A White House statement issued days after the capture of Maduro
claims that the United States
“needs” Greenland
and that acquiring the territory is a “national security priority.”
👉What is so troubling about the Trump administration’s words and actions is not just that the administration is breaking the law.
-- And it is:
⚠️the intervention in Venezuelaclearly violates the UN Charter’s prohibition on the use of force.
But more than that,
❌ U.S. officials have discarded the idea of legal constraints altogether.
The only constraint, Trump said in an interview with The New York Times last week,
is his “own morality.”
There is no real argument to defend the government’s behavior.
No pretense.
No attempt to persuade.
When a policy is announced in an online post,
without explanation or justification,
one has the unsettling sense that its makers see no need to bother cloaking it with a lie.
A system of #rules can survive some hypocrisy,
but #nihilism will bring it down.
At the same time,
the Trump administration is acting as though the threat or use of force alone can grant it legal entitlements.
#Gunboat #diplomacy, roundly renounced when war was outlawed,
has returned.
The United States is using oil blockades, coercive seizures, and military threats
to extract political and economic concessions from other countries.
This is an attempt to assert that power alone creates rights, regardless of reason.
🔥A world in which the powerful no longer feel the need to justify themselves is not merely unjust.
-- It is barbaric:
Operations to kill, steal, and destroy are severed from any claim of right.
That world does not have a legal order at all.
It has only force,
guided by one man’s whims.
https://www.foreignaffairs.com/united-states/world-without-rules
US attack on Venezuela raises fears of future Greenland takeover
#HackerNews #USattack #Venezuela #Greenland #takeover #fears #Diplomacy #InternationalRelations
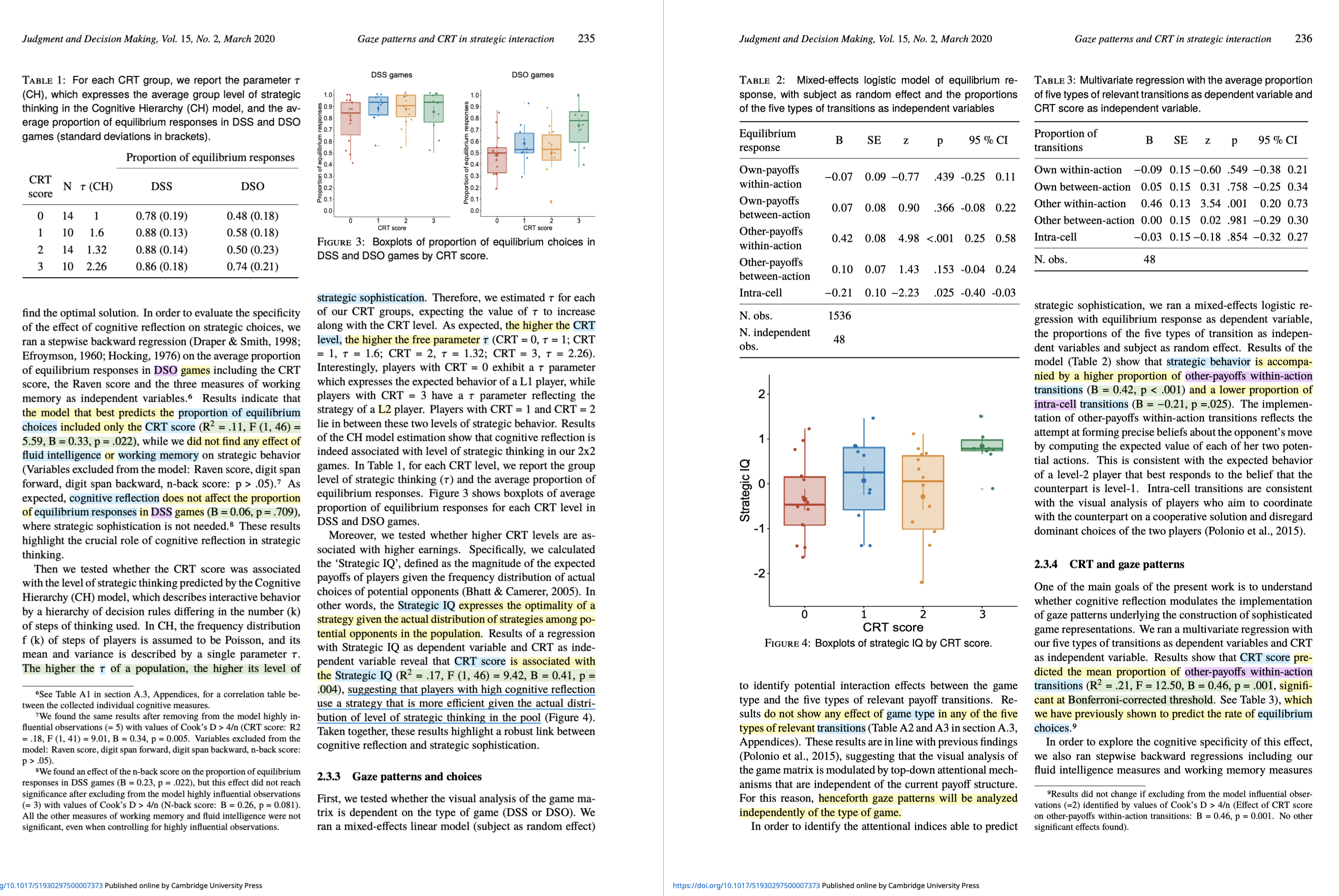
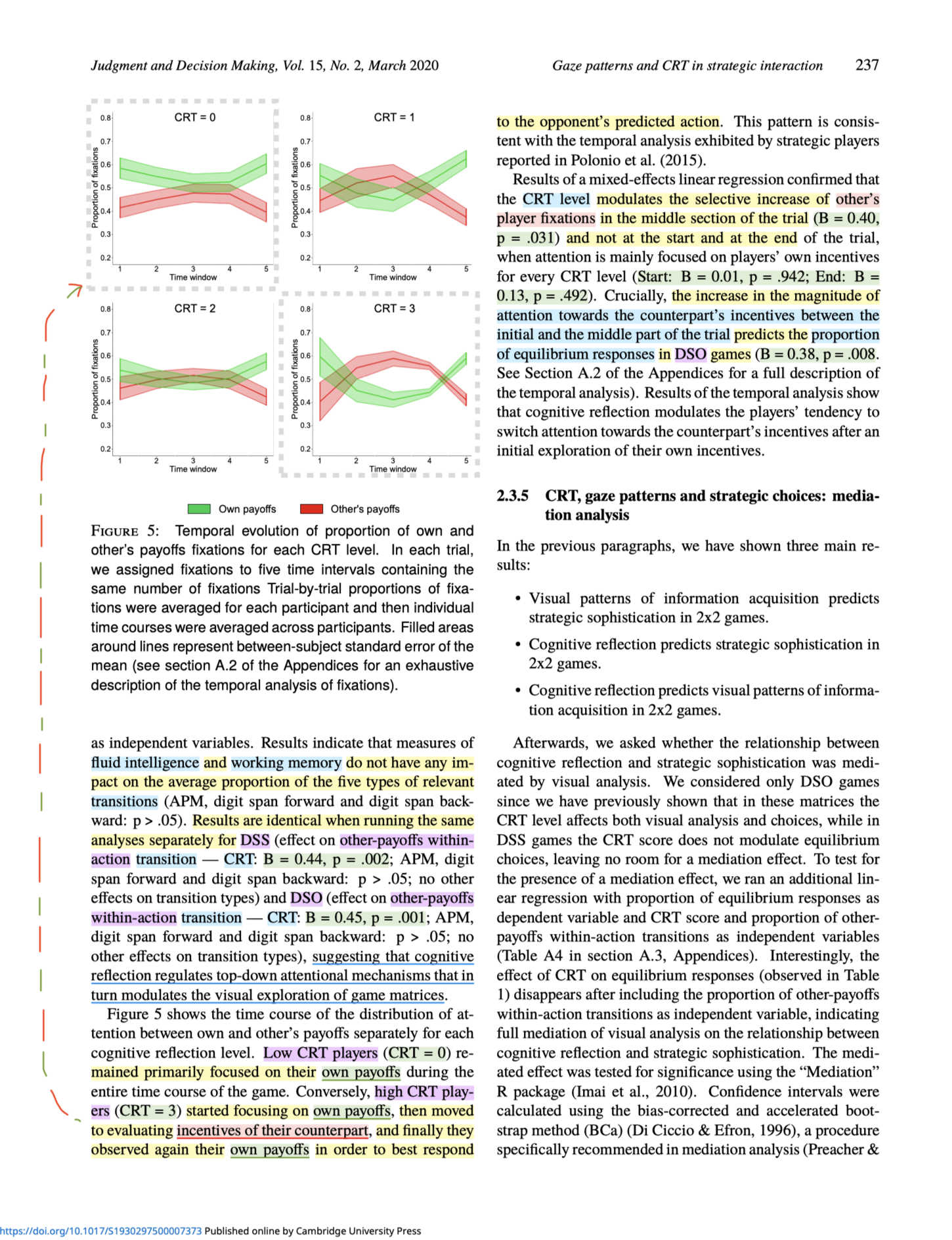
Are more reflective thinkers better at games that require empathy or perspective-taking?
In two experiments, reflective thinkers performed better on such games, seemingly because they paid more attention to the other players' incentives.
https://doi.org/10.1017/S1930297500007373
#econ #cogSci #psychology #relationships #negotiation #diplomacy #geopolitics #intelligence #defense #security #policy
My opinion - Foreign media in countries like #Australia, where this piece ran, shouldn't publish #Chinese government op-eds unless #China's state media publishes foreign diplomat op-eds.
#Reciprocity is a basic tenet of #diplomacy and should be enforced in the #digital and #media spaces.
Chinese consulates regularly conduct gray-zone operations in the form of “pop-up” events at nondesignated diplomatic facilities. https://www.japantimes.co.jp/commentary/2025/11/19/japan/chinas-gray-zone-activities-in-japan/?utm_medium=Social&utm_source=mastodon #commentary #japan #china #chinajapanrelations #grayzoneoperations #diplomacy
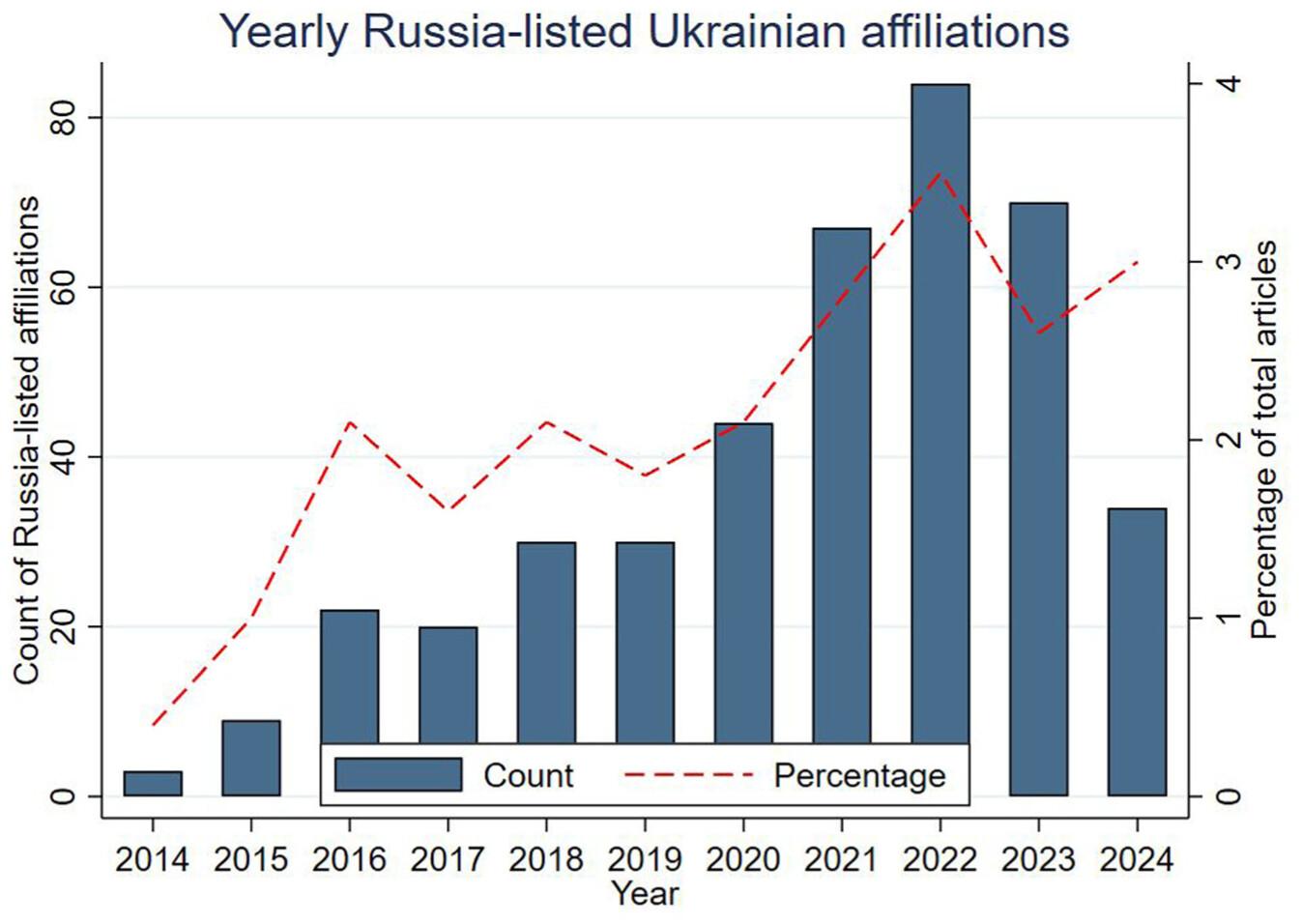
A new study by 🇨🇭 researcher analysed nearly 18,000 #PubMed papers and found 413 cases where Ukrainian cities were incorrectly listed as Russian, mostly #Simferopol and #Sevastopol:
 https://doi.org/10.1177/01655515251388044
https://doi.org/10.1177/01655515251388044
The work shows a clear post-2014 rise in such misattributions and highlights how #war shape academic metadata. A concise and rigorous contribution to understanding the visibility of Ukrainian research.
#Science #Diplomacy #Ukraine #Research #ScholarlyCommunication
Geopolitical conflict and author affiliation: Designation of Ukrainian cities under Russia in academic publishing
A new study by 🇨🇭 researcher analysed nearly 18,000 #PubMed papers and found 413 cases where Ukrainian cities were incorrectly listed as Russian, mostly #Simferopol and #Sevastopol:
 https://doi.org/10.1177/01655515251388044
https://doi.org/10.1177/01655515251388044
The work shows a clear post-2014 rise in such misattributions and highlights how #war shape academic metadata. A concise and rigorous contribution to understanding the visibility of Ukrainian research.
#Science #Diplomacy #Ukraine #Research #ScholarlyCommunication
Geopolitical conflict and author affiliation: Designation of Ukrainian cities under Russia in academic publishing
US declines to join more than 70 countries in signing UN cybercrime treaty
https://therecord.media/us-declines-signing-cybercrime-treaty?
#HackerNews #US #cybercrime #treaty #UN #treaty #international #relations #cybersecurity #diplomacy
this's remarkably good on hegemony post trump
"Hegemony is not a birthright. It is a practice, renewed daily by choices—some grand, some mundane. The U.S. had immense resources, allies, and reservoirs of goodwill in 2016. But these assets have and are now being squandered at an extraordinarily rapid rate, definitely in part by simple malice, but even more so by neglect, confusion, and the ever-present temptation to turn inward"
#internationalRelations #hegemony #diplomacy #politics
https://braddelong.substack.com/p/a-note-on-the-closing-of-the-path
this's remarkably good on hegemony post trump
"Hegemony is not a birthright. It is a practice, renewed daily by choices—some grand, some mundane. The U.S. had immense resources, allies, and reservoirs of goodwill in 2016. But these assets have and are now being squandered at an extraordinarily rapid rate, definitely in part by simple malice, but even more so by neglect, confusion, and the ever-present temptation to turn inward"
#internationalRelations #hegemony #diplomacy #politics
https://braddelong.substack.com/p/a-note-on-the-closing-of-the-path
U.S. Vice President JD Vance says America’s strikes on Iran show military power succeeding where diplomacy failed — but history since the Cold War shows most such attempts flop. https://www.japantimes.co.jp/commentary/2025/07/18/world/trump-doctrine-is-wishful-thinking/?utm_medium=Social&utm_source=mastodon #commentary #worldnews #donaldtrump #us #defense #diplomacy #iran #iraq #serbia
#Trump#Defense Secy #PeteHegseth echoed his remarks in a press conference.
“I can only confirm that there are both public & private messages being directly delivered to the Iranians in multiple channels, giving them every opportunity to come to the table,” #Hegseth said.